Note: This article is the first part of a three part series. The next part is here.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, businesses are reaping unprecedented benefits from the flexibility, scalability, and innovation that cloud services provide. However, with these advantages comes a significant challenge: managing cloud costs effectively. Enter FinOps, a transformative practice designed to bridge the gap between finance, operations, and technology. In this article, we’ll explore what FinOps is, why it’s essential, and how organizations can implement it to optimize their cloud investments.

What is FinOps?
FinOps, short for Financial Operations, is a practice that combines financial management principles with the operational efficiencies of DevOps. At its core, FinOps is about creating a culture of accountability and collaboration between engineering, finance, and business teams to manage cloud spend effectively. It involves continuous monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing cloud usage to ensure that every dollar spent brings maximum value.
The Phases of FinOps
FinOps implementation is typically broken down into three distinct phases, each building upon the other to create a cohesive and effective strategy:
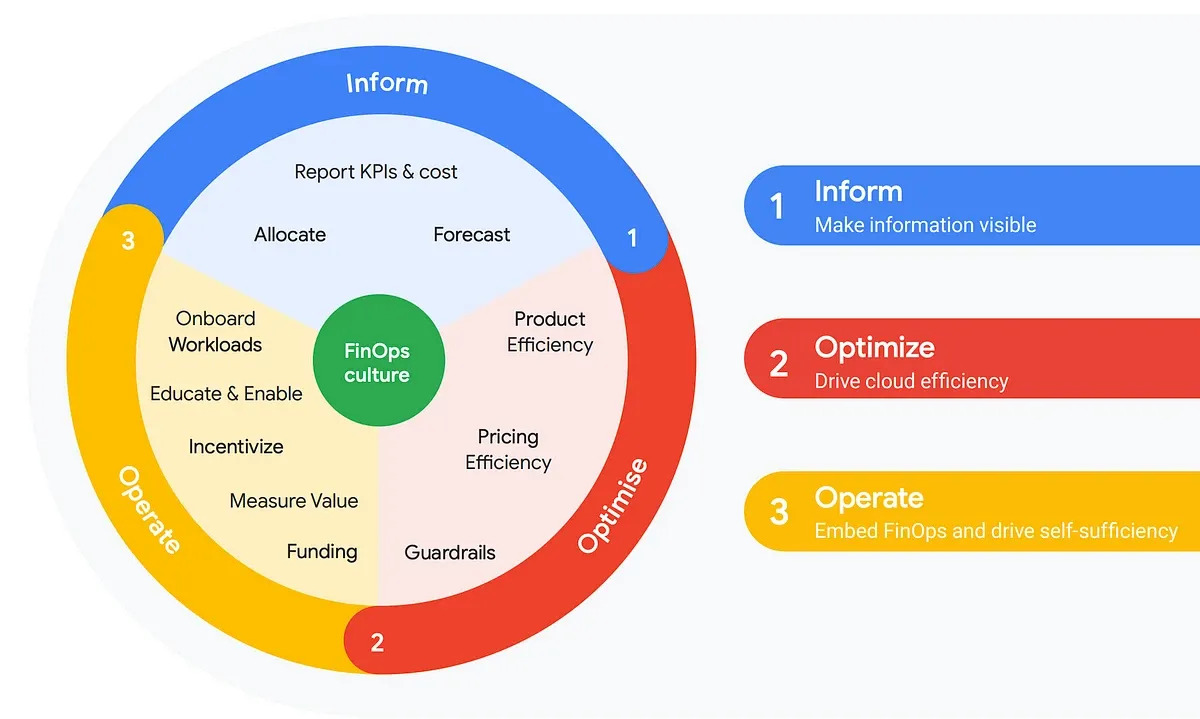
Inform
This phase is about achieving visibility and transparency into cloud usage and costs. It involves setting up the necessary tools and processes to collect data and generate reports. Key activities include tracking cloud spend, establishing cost allocation and tagging strategies, and creating dashboards for real-time insights.
Optimize
With visibility in place, the next phase focuses on cost optimization. This includes identifying inefficiencies, such as underutilized resources or redundant services, and implementing strategies to reduce waste. Activities in this phase might include rightsizing instances, scheduling non-essential resources to shut down during off-hours, and leveraging discounts and reserved instances.
Operate
The final phase is about operationalizing FinOps practices and embedding them into the organization’s culture. This includes continuous monitoring and improvement, regular reviews of cloud costs and usage, and fostering a culture of accountability. Key activities include setting up governance policies, conducting cost audits, and ensuring all teams are aligned with FinOps principles.
The Core Principles of FinOps
FinOps is built on three core principles
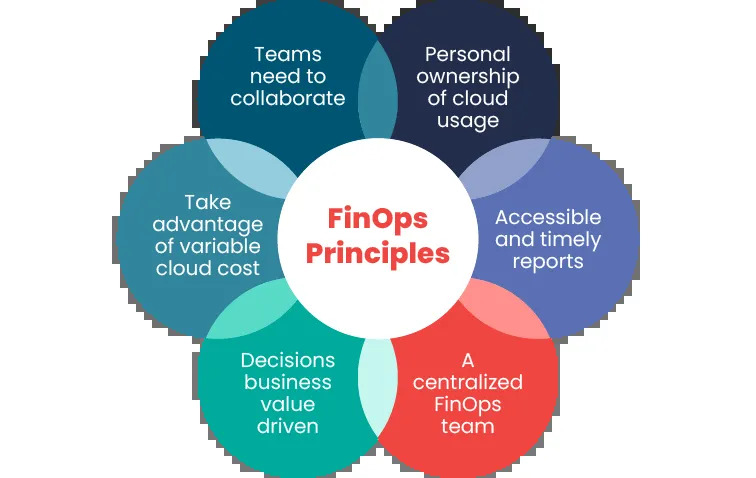
1. Collaboration: FinOps requires a collaborative effort across finance, operations, and technology teams. This ensures that financial decisions are made with a full understanding of the technical requirements and implications.
2. Ownership: Engineering and development teams are given ownership of their cloud usage and costs, encouraging them to take responsibility for optimizing their spend.
3. Continuous Improvement: FinOps is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. It involves continuous monitoring, analysis, and optimization to ensure that cloud investments are always aligned with business goals.
Why is FinOps Important?
The shift to cloud computing has brought unprecedented flexibility and scalability. However, it also introduces complexity in managing costs. Traditional budgeting methods are often ill-equipped to handle the dynamic nature of cloud spending. Here’s why FinOps is essential:
Cost Control: FinOps helps prevent cloud overspend by identifying and mitigating inefficiencies.
Agility: It supports rapid innovation by providing teams with the financial insights needed to make quick, data-driven decisions.
Accountability: By making costs visible and attributable to specific teams or projects, FinOps ensures that everyone is accountable for their cloud usage and spending.
Implementing FinOps in Your Organization
Adopting FinOps requires a shift in mindset and processes. Here are some steps to get started:
1. Establish a FinOps Team: Form a cross-functional team with representatives from finance, engineering, and business units. This team will be responsible for driving FinOps initiatives and ensuring collaboration across departments.
2. Set Clear Goals: Define what success looks like for your FinOps practice. This could include specific cost-saving targets, efficiency improvements, or other KPIs.
3. Leverage Tools and Automation: Use FinOps tools to gain insights into cloud usage and costs. Automation can help streamline processes such as cost allocation, budget alerts, and optimization recommendations.
4. Educate and Empower Teams: Provide training and resources to help teams understand the importance of FinOps and how they can contribute to cost-efficiency. Empower them with the tools and data they need to make informed decisions.
5. Continuous Improvement: FinOps is not a one-time project but an ongoing practice. Regularly review and refine your processes, metrics, and goals to adapt to changing business needs and cloud environments.
Real-World Impact of FinOps
Many organizations have successfully implemented FinOps to achieve significant cost savings and operational efficiencies. For instance, media company **A** reduced their cloud spend by 25% in the first year of adopting FinOps. By continuously monitoring their usage and implementing automated cost-optimization strategies, they were able to eliminate waste and invest more in innovation.
Tech giant **B** used FinOps to gain better visibility into their cloud costs across various departments. This transparency enabled them to allocate budgets more accurately and hold teams accountable for their spending, leading to a more efficient and predictable financial model.
Conclusion
As cloud adoption continues to grow, so does the need for effective financial management. FinOps offers a robust framework to manage cloud costs, drive efficiency, and foster a culture of accountability. By unifying finance and DevOps, FinOps ensures that cloud spending is aligned with business goals and maximizes the value of your cloud investment.
If your organization is looking to optimize its cloud strategy, consider embracing FinOps. It’s not just about cutting costs — it’s about making smarter, data-driven decisions that support your business’s growth and innovation.
Note: This article is the first part of a three part series. The next part is here.